ROLE MAINTENANCE
As with most solutions in Splunk, there are many strategies to manage roles. I suggest the following:
Only create a role in Splunk when you need it.
In other words, don’t add roles to Splunk until you actually need to add users to those roles. We’ve worked with a lot of customers who have created 20 or more roles in anticipation of future growth but only assigned users to three. This creates an unnecessary mess, as well as a possible security risk should someone inadvertently be assigned to a previously unused role.
The time to integrate with LDAP / AD is now.
If you are using Splunk in a production environment, manage your users with LDAP / AD. We’ve encountered a few customers who have managed over 100 users in Splunk without LDAP / AD. This quickly grows out of control and can create a security risk when users leave the company or change roles.
Using Splunk to manage users, you’ll inevitably have orphaned users, users with access to data they shouldn’t see, and more admins than you need. An audit for on customer who used Spunk managed accounts showed that 60% of the Splunk users no longer worked for the company, yet their Splunk accounts were still active.
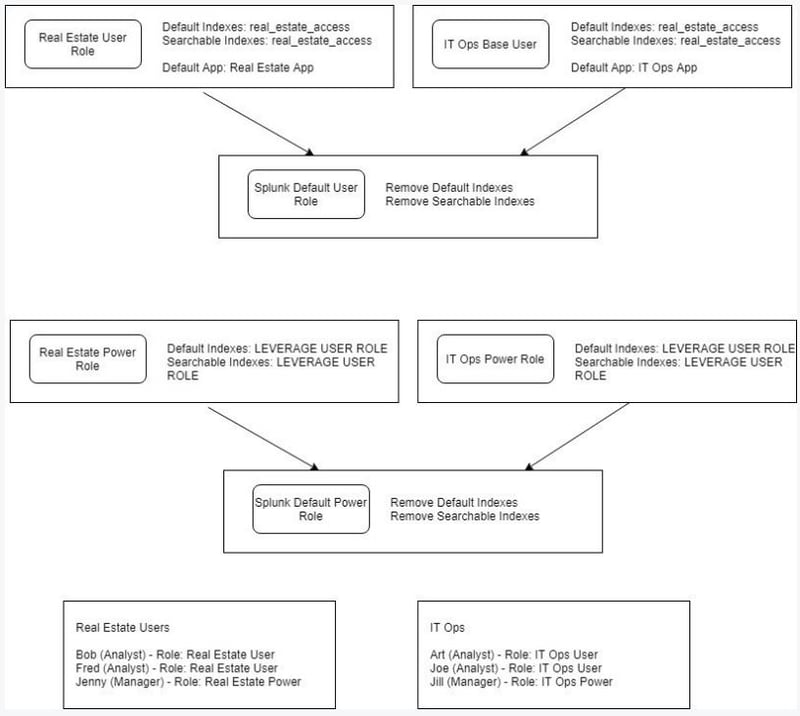
Create a role for each logical user group.
A logical user can be thought of as a group of Splunk users who will generally use the same searches or work with the same data. A role for each logical user group allows you to assign apps, indexes and other permissions to users based on the work they do.
For example, if I have a group of users that use Splunk to analyze real estate analytics, I will create a role for that group of users and assign those users to that role. I won’t assign the users to Splunk’s default User or Power User roles.
This may sound trivial, but we’ve encountered a number of customers who are assigning user permissions using Splunk’s built in roles (user, power user, etc.). This is not granular enough to manage access to apps, indexes, searches, etc.
If your user groups contain users that require different levels of permissions overlay a role with those permissions onto the user group’s base role. Don’t duplicate base role attributes in these roles. The graphic at the end of this document describes the complete model for user and role management.
INDEX ACCESS CONTROL
Expanding on our recommended model to manage users and roles, we suggest that you manage index access within the roles associated Logical User Groups level instead of within the Splunk User and Power roles.
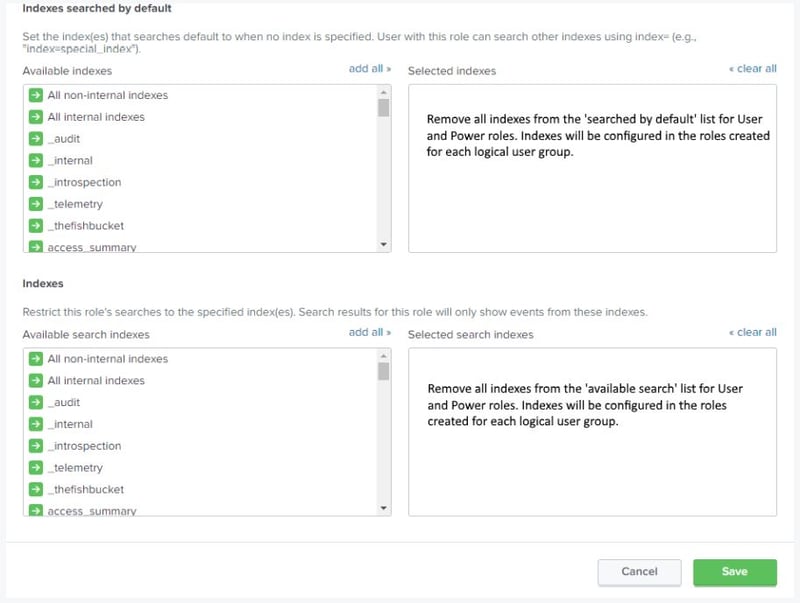
Remove all index access from the Splunk User and Power roles. For the built-in Splunk User and Power roles remove all indexes in the ‘Indexes searched by default’ and ‘Indexes’ tabs near the bottom of the Access Controls -> Roles dashboard.
Assign the necessary indexes to the Splunk role associated with each Logical User Group. If you find that different users within a Logical User Group require access to different indexes, you have two options, depending on your level of openness.
If you are comfortable with users accessing more data than is required, assign all necessary indexes to the role associated with the Logical User Group.
If you require more granularity create multiple overlay roles, each containing the minimum required indexes. The overlay roles will be assigned to the subset of users that require access to specific indexes.
Alternatively, we work with a few Splunk users who have assigned an individual Splunk role to each index and then leveraged their Identity Management Solution, such as Sail Point, to assign index access to each user. While we do not believe there is a technical advantage to this approach, your Identity Management Solution will provide auditing and reporting that isn’t available in Splunk.
CREATE A SPLUNK APP FOR EACH LOGICAL USER GROUP
Left to their own accord, most Splunk users will save searches in the Search App. While this isn’t technically a problem, it can become a management nightmare if you have hundreds or thousands of searches all saved into a single App.
To solve this problem, we recommend creating a separate Splunk App for each logical user group. As defined in the role section, a logical user can be thought of a group of Splunk users who will generally use the same searches or work with the same data.
Within the App Management Dashboard, configure the App permissions to only allow the Splunk role associated with this app to have access. Because this app is effectively a user workspace, give the role read and write access. You may also want to give the Admin read and write permissions as well. Set config-file sharing to ‘This app only.’
Lastly, be sure to update the Default App for each role to be the associated app.
Your users will now have a clean workspace shared by their colleagues and no one else.
CONCLUSION
Because Splunk is a flexible platform there is no enforced structure for managing users and roles. While this can lead to an unorganized and chaotic system, we hope that following the suggestions in article gives you a foundation to securely and effectively manage access to Splunk.
Download our list of reference searches for more tips on managing your Splunk users and roles.



